 SpringBoot 监控神器——Actuator 保姆级教程
SpringBoot 监控神器——Actuator 保姆级教程
# SpringBoot 整合 actuator
SpringBoot 自带监控功能 Actuator,可以帮助实现对程序内部运行情况监控,比如监控状况、Bean 加载情况、环境变量、日志信息、线程信息等
# 配置 Actuator
#
pom.xml
<!-- web start-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- web end-->
<!-- actuator start-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- actuator end-->
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
- 浏览器打开链接 http://localhost:8080/actuator/
可以看到所有支持的连接,默认只有
/actuator
/actuator/health
/actuator/health/{component}
/actuator/health/{component}/{instance}
/actuator/info
2
3
4
5
- bean 加载情况 http://localhost:8080/actuator/beans
具体的使用方法:
引入上述的依赖 jar
通过下面的配置启用所有的监控端点,默认情况下,这些端点是禁用的;
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
“*”号代表启用所有的监控端点,可以单独启用,例如,`health`,`info`,`metrics`等
2
3
4
5
6
# Actuator 的 REST 接口
Actuator 监控分成两类:原生端点和用户自定义端点;自定义端点主要是指扩展性,用户可以根据自己的实际应用,定义一些比较关心的指标,在运行期进行监控。
原生端点是在应用程序里提供众多 Web 接口,通过它们了解应用程序运行时的内部状况。原生端点又可以分成三类:
应用配置类:可以查看应用在运行期的静态信息:例如自动配置信息、加载的 springbean 信息、yml 文件配置信息、环境信息、请求映射信息;
度量指标类:主要是运行期的动态信息,例如堆栈、请求连、一些健康指标、metrics 信息等;
操作控制类:主要是指 shutdown, 用户可以发送一个请求将应用的监控功能关闭。
Actuator 提供了 13 个接口,具体如下表所示。
| GET | /auditevents | 显示应用暴露的审计事件 (比如认证进入、订单失败) |
|---|---|---|
| GET | /beans | 描述应用程序上下文里全部的 Bean,以及它们的关系 |
| GET | /conditions | 就是 1.0 的 /autoconfig ,提供一份自动配置生效的条件情况,记录哪些自动配置条件通过了,哪些没通过 |
| GET | /configprops | 描述配置属性 (包含默认值) 如何注入 Bean |
| GET | /env | 获取全部环境属性 |
| GET | /env/{name} | 根据名称获取特定的环境属性值 |
| GET | /flyway | 提供一份 Flyway 数据库迁移信息 |
| GET | /liquidbase | 显示 Liquibase 数据库迁移的纤细信息 |
| GET | /health | 报告应用程序的健康指标,这些值由 HealthIndicator 的实现类提供 |
| GET | /heapdump | dump 一份应用的 JVM 堆信息 |
| GET | /httptrace | 显示 HTTP 足迹,最近 100 个 HTTP request/repsponse |
| GET | /info | 获取应用程序的定制信息,这些信息由 info 打头的属性提供 |
| GET | /logfile | 返回 log file 中的内容 (如果 logging.file 或者 logging.path 被设置) |
| GET | /loggers | 显示和修改配置的 loggers |
| GET | /metrics | 报告各种应用程序度量信息,比如内存用量和 HTTP 请求计数 |
| GET | /metrics/{name} | 报告指定名称的应用程序度量值 |
| GET | /scheduledtasks | 展示应用中的定时任务信息 |
| GET | /sessions | 如果我们使用了 Spring Session 展示应用中的 HTTP sessions 信息 |
| POST | /shutdown | 关闭应用程序,要求 endpoints.shutdown.enabled 设置为 true |
| GET | /mappings | 描述全部的 URI 路径,以及它们和控制器 (包含 Actuator 端点) 的映射关系 |
| GET | /threaddump | 获取线程活动的快照 |
# 命令详解
在 Spring Boot 2.x 中为了安全期间,Actuator 只开放了两个端点 /actuator/health 和 /actuator/info。可以在配置文件中设置打开。
可以打开所有的监控点
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
2
3
4
5
也可以选择打开部分
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
exclude: beans,trace
2
3
4
5
Actuator 默认所有的监控点路径都在 / actuator/*,当然如果有需要这个路径也支持定制。
management:
endpoints:
web:
base-path: /manage #记得要加上/
2
3
4
设置完重启后,再次访问地址就会变成 / manage/*
Actuator 几乎监控了应用涉及的方方面面,我们重点讲述一些经常在项目中常用的命令。
# health
health 主要用来检查应用的运行状态,这是我们使用最高频的一个监控点。通常使用此接口提醒我们应用实例的运行状态,以及应用不” 健康 “的原因,比如数据库连接、磁盘空间不够等。
默认情况下 health 的状态是开放的,添加依赖后启动项目,访问:http://localhost:8080/actuator/health 即可看到应用的状态。
{
"status" : "UP"
}
2
3
要想查看详细的应用健康信息需要配置 management.endpoint.health.show-details 的值为 always,配置之后我们再次访问 http://localhost:8080/actuator/health,获取的信息如下:
{
"status": "UP",
"components": {
"diskSpace": {
"status": "UP",
"details": {
"total": 236510507008,
"free": 223361744896,
"threshold": 10485760
}
},
"ping": {
"status": "UP"
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
Spring boot 的健康信息都是从 ApplicationContext 中的各种 HealthIndicator Beans 中收集到的,Spring boot 框架中包含了大量的 HealthIndicators 的实现类,当然你也可以实现自己认为的健康状态。
默认情况下,最终的 Spring Boot 应用的状态是由 HealthAggregator 汇总而成的,汇总的算法是:
- 1 设置状态码顺序:setStatusOrder(Status.DOWN, Status.OUT_OF_SERVICE, Status.UP, Status.UNKNOWN);。
- 2 过滤掉不能识别的状态码。
- 3 如果无任何状态码,整个 Spring Boot 应用的状态是 UNKNOWN。
- 4 将所有收集到的状态码按照 1 中的顺序排序。
- 5 返回有序状态码序列中的第一个状态码,作为整个 Spring Boot 应用的状态。
health 通过合并几个健康指数检查应用的健康情况。Spring boot 框架自带的 HealthIndicators 目前包括:
| CassandraHealthIndicator | Checks that a Cassandra database is up. |
|---|---|
DiskSpaceHealthIndicator | Checks for low disk space. |
DataSourceHealthIndicator | Checks that a connection to DataSource can be obtained. |
ElasticsearchHealthIndicator | Checks that an Elasticsearch cluster is up. |
InfluxDbHealthIndicator | Checks that an InfluxDB server is up. |
JmsHealthIndicator | Checks that a JMS broker is up. |
MailHealthIndicator | Checks that a mail server is up. |
MongoHealthIndicator | Checks that a Mongo database is up. |
Neo4jHealthIndicator | Checks that a Neo4j server is up. |
RabbitHealthIndicator | Checks that a Neo4j server is up. |
RedisHealthIndicator | Checks that a Redis server is up. |
SolrHealthIndicator | Checks that a Solr server is up. |
举个例子,如果你的应用使用 Redis,RedisHealthindicator 将被当作检查的一部分;如果使用 MongoDB,那么 MongoHealthIndicator 将被当作检查的一部分。
可以在配置文件中关闭特定的健康检查指标,比如关闭 redis 的健康检查:
management:
health:
redise:
enabled: false
2
3
4
默认,所有的这些健康指标被当作健康检查的一部分。
自定义 HealthIndicator 健康检查
有时候需要提供自定义的健康状态检查信息,你可以通过实现 HealthIndicator 的接口来实现,并将该实现类注册为 spring bean。你需要实现其中的 health() 方法,并返回自定义的健康状态响应信息,该响应信息应该包括一个状态码和要展示详细信息。例如,下面就是一个接口 HealthIndicator 的实现类:
@Component
public class MyHealthIndicator implements HealthIndicator {
@Override
public Health health() {
int errorCode = check(); // perform some specific health check
if (errorCode != 0) {
return Health.down().withDetail("Error Code", errorCode).build();
}
return Health.up().build();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
另外,除了 Spring boot 定义的几个状态类型,我们也可以自定义状态类型,用来表示一个新的系统状态。在这种情况下,你还需要实现接口 HealthAggregator ,或者通过配置 management.health.status.order 来继续使用 HealthAggregator 的默认实现。
例如,在你自定义的健康检查 HealthIndicator 的实现类中,使用了自定义的状态类型 FATAL,为了配置该状态类型的严重程度,你需要在 application 的配置文件中添加如下配置:
management:
health:
status:
order: FATAL, DOWN, OUT_OF_SERVICE, UNKNOWN, UP
2
3
4
在做健康检查时,响应中的 HTTP 状态码反应了整体的健康状态,(例如,UP 对应 200, 而 OUT_OF_SERVICE 和 DOWN 对应 503)。同样,你也需要为自定义的状态类型设置对应的 HTTP 状态码,例如,下面的配置可以将 FATAL 映射为 503(服务不可用):
management:
health:
status:
http-mapping:
FATAL: 503
2
3
4
5
下面是内置健康状态类型对应的 HTTP 状态码列表:
| Status | Mapping |
|---|---|
| OUT_OF_SERVICE | SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE (503) |
| DOWN | SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE (503) |
| UP | No mapping by default, so http status is 200 |
| UNKNOWN | No mapping by default, so http status is 200 |
# info
info 就是我们自己配置在配置文件中以 info 开头的配置信息,比如我们在示例项目中的配置是:
info:
app:
name:
spring-boot-actuator
version: 1.0.0
test: test
2
3
4
5
6
启动示例项目,访问:http://localhost:8080/actuator/info 返回部分信息如下:
{
"app": {
"name": "spring-boot-actuator",
"version": "1.0.0",
"test":"test"
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
# beans
根据示例就可以看出,展示了 bean 的别名、类型、是否单例、类的地址、依赖等信息。
启动示例项目,访问:http://localhost:8080/actuator/beans返回部分信息如下:
[
{
"context": "application:8080:management",
"parent": "application:8080",
"beans": [
{
"bean": "embeddedServletContainerFactory",
"aliases": [
],
"scope": "singleton",
"type": "org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.tomcat.TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory",
"resource": "null",
"dependencies": [
]
},
{
"bean": "endpointWebMvcChildContextConfiguration",
"aliases": [
],
"scope": "singleton",
"type": "org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.EndpointWebMvcChildContextConfiguration$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$a4a10f9d",
"resource": "null",
"dependencies": [
]
}
}
]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
# conditions
Spring Boot 的自动配置功能非常便利,但有时候也意味着出问题比较难找出具体的原因。使用 conditions 可以在应用运行时查看代码了某个配置在什么条件下生效,或者某个自动配置为什么没有生效。
启动示例项目,访问:http://localhost:8080/actuator/conditions 返回部分信息如下:
{
"positiveMatches": {
"DevToolsDataSourceAutoConfiguration": {
"notMatched": [
{
"condition": "DevToolsDataSourceAutoConfiguration.DevToolsDataSourceCondition",
"message": "DevTools DataSource Condition did not find a single DataSource bean"
}
],
"matched": [ ]
},
"RemoteDevToolsAutoConfiguration": {
"notMatched": [
{
"condition": "OnPropertyCondition",
"message": "@ConditionalOnProperty (spring.devtools.remote.secret) did not find property 'secret'"
}
],
"matched": [
{
"condition": "OnClassCondition",
"message": "@ConditionalOnClass found required classes 'javax.servlet.Filter', 'org.springframework.http.server.ServerHttpRequest'; @ConditionalOnMissingClass did not find unwanted class"
}
]
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# heapdump
返回一个 GZip 压缩的 JVM 堆 dump
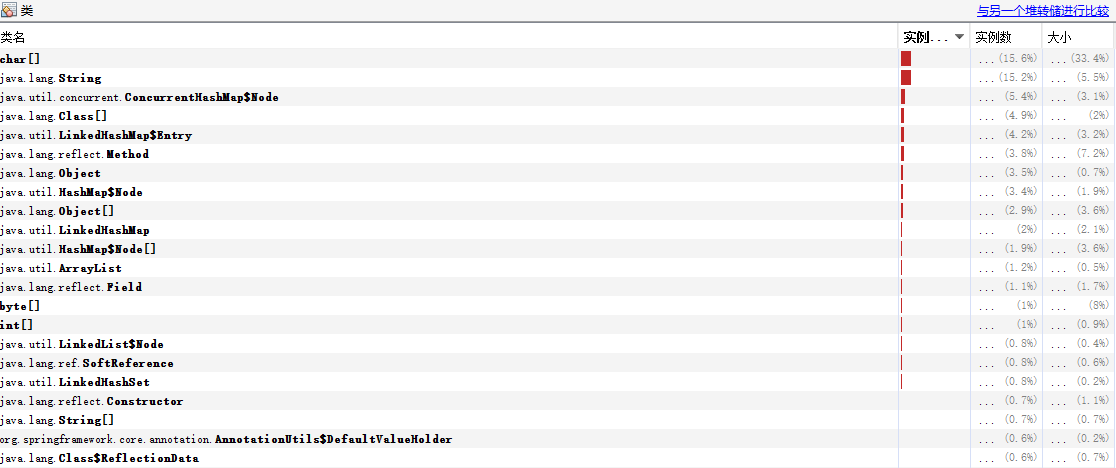
启动示例项目,访问:http://localhost:8080/actuator/heapdump 会自动生成一个 Jvm 的堆文件 heapdump,我们可以使用 JDK 自带的 Jvm 监控工具 VisualVM 打开此文件查看内存快照。类似如下图:
# shutdown
开启接口优雅关闭 Spring Boot 应用,要使用这个功能首先需要在配置文件中开启:
management:
endpoint:
shutdown:
enabled: true
2
3
4
配置完成之后,启动示例项目,使用 curl 模拟 post 请求访问 shutdown 接口。
shutdown 接口默认只支持 post 请求。
curl -X POST "http://localhost:8080/actuator/shutdown"
{
"message": "Shutting down, bye..."
}
2
3
4
此时你会发现应用已经被关闭。
# mappings
描述全部的 URI 路径,以及它们和控制器的映射关系
启动示例项目,访问:http://localhost:8080/actuator/mappings返回部分信息如下:
{
"/**/favicon.ico": {
"bean": "faviconHandlerMapping"
},
"{[/hello]}": {
"bean": "requestMappingHandlerMapping",
"method": "public java.lang.String com.neo.controller.HelloController.index()"
},
"{[/error]}": {
"bean": "requestMappingHandlerMapping",
"method": "public org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity<java.util.Map<java.lang.String, java.lang.Object>> org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.BasicErrorController.error(javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest)"
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# threaddump
/threaddump 接口会生成当前线程活动的快照。这个功能非常好,方便我们在日常定位问题的时候查看线程的情况。 主要展示了线程名、线程 ID、线程的状态、是否等待锁资源等信息。
启动示例项目,访问:http://localhost:8080/actuator/threaddump 返回部分信息如下:
[
{
"threadName": "http-nio-8088-exec-6",
"threadId": 49,
"blockedTime": -1,
"blockedCount": 0,
"waitedTime": -1,
"waitedCount": 2,
"lockName": "java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer$ConditionObject@1630a501",
"lockOwnerId": -1,
"lockOwnerName": null,
"inNative": false,
"suspended": false,
"threadState": "WAITING",
"stackTrace": [
{
"methodName": "park",
"fileName": "Unsafe.java",
"lineNumber": -2,
"className": "sun.misc.Unsafe",
"nativeMethod": true
},
...
{
"methodName": "run",
"fileName": "TaskThread.java",
"lineNumber": 61,
"className": "org.apache.tomcat.util.threads.TaskThread$WrappingRunnable",
"nativeMethod": false
}
...
],
"lockInfo": {
"className": "java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer$ConditionObject",
"identityHashCode": 372286721
}
}
...
]
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
生产出现问题的时候,可以通过应用的线程快照来检测应用正在执行的任务。
# loggers 端点
访问 http://localhost:8080/actuator/loggers 可以查看当前应用的日志级别等信息:
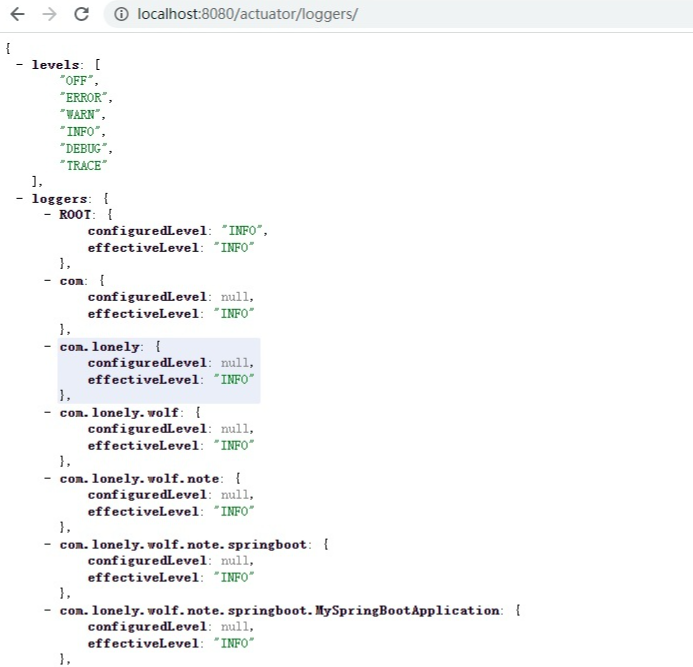
这里面本身并不特别,但是有一个功能却非常有用,比如我们生产环境日志级别一般都是 info,但是现在有一个 bug 通过 info 级别无法排查,那么我们就可以临时修改 log 级别。
比如上图中的 ROOT 节点是 info 级别,那么我们可以通过 postman 等工具来发一个 post 请求修改日志级别。
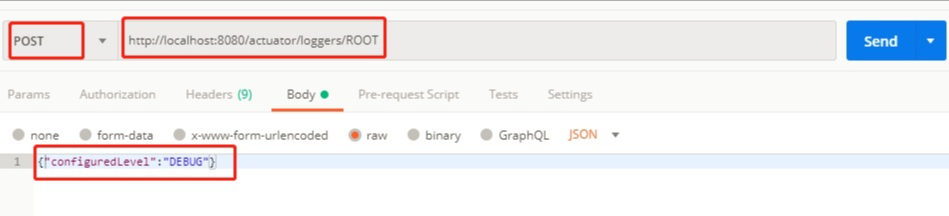
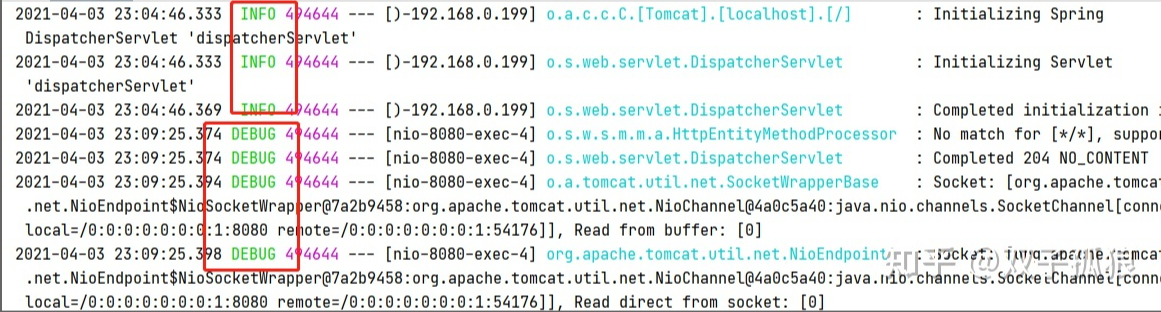
修改之后就会发现,日志由原来的 info 变成了 debug:
# metrics 端点
metrics 是一个非常重要的监控端点,其监控内容覆盖了 JVM 内存、堆、类加载、处理器和 tomcat 容器等一些重要指标:
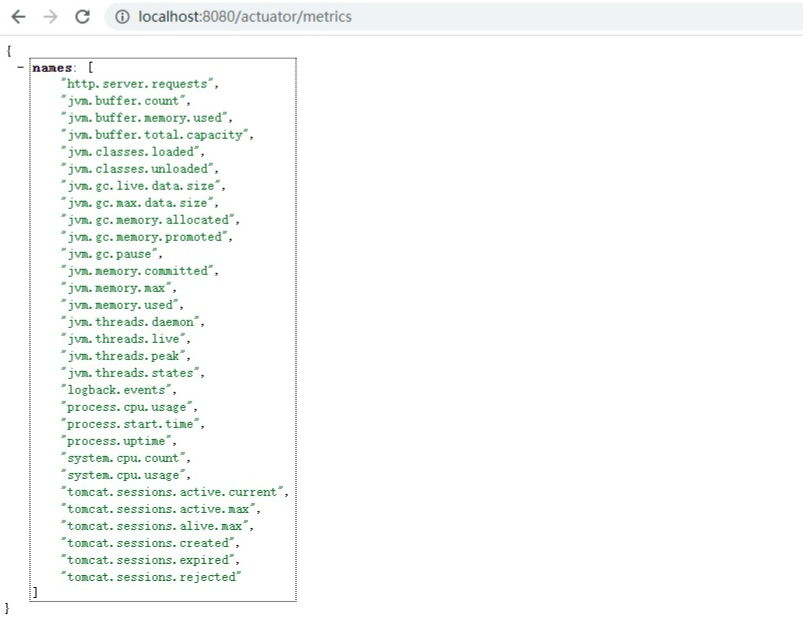
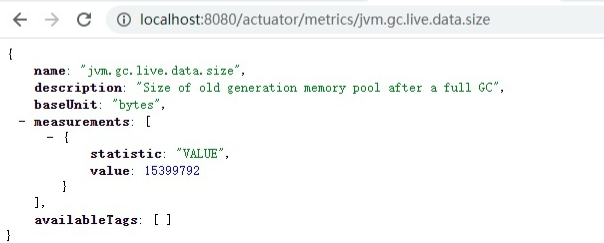
可以看到这里面包含了非常多的指标,任意访问一个指标就可以查看对应的指标信息:
# 自定义 Endpoint
自定义配置来控制是否开启过滤
actuator:
filter:
switch: false
2
3
# 自定义监控端点常用注解
自定义一个监控端点主要有如下常用注解:
- @Endpoint:定义一个监控端点,同时支持
HTTP和JMX两种方式。 - @WebEndpoint:定义一个监控端点,只支持
HTTP方式。 - @JmxEndpoint:定义一个监控端点,只支持
JMX方式。
以上三个注解作用在类上,表示当前类是一个监控端点,另外还有一些注解会用在方法和参数上:
- @ReadOperation:作用在方法上,可用来返回端点展示的信息(通过
Get方法请求)。 - @WriteOperation:作用在方法上,可用来修改端点展示的信息(通过
Post方法请求)。 - @DeleteOperation:作用在方法上,可用来删除对应端点信息(通过
Delete方法请求)。 - @Selector:作用在参数上,用来定位一个端点的具体指标路由。
一般情况下,是没必要自定义 Endpoint 的,但是也不排除特殊情况,我这里自定义一个 Endpoint,用来往 request 里放一个 user 对象,这个 user 是用来做测试的,用于下面突破 filter 用的(下面再说),这里先说怎么增查这个 user。
过程如下: - 使用 @Endpoint 注解相应的类,作为 Actuator 的一个 endpoint。注解要指定 id,这个 id 作为访问路径,比如这里是 / actuator/super; - @ReadOperation 来注解查询接口,如果要根据路径做查询,要用 @Selector 注解方法参数;注意这地方是@Selector String arg0,这个 arg0 不能改变,改成其他的,开放出去的接口还是 /{arg0},这就导致你的方法无法正常获取参数值。 - @WriteOperation 来注解修改接口,注意请求数据必须是 json,而且参数不像 controller 中那么灵活,不能将实体作为参数,要把实体中相应的属性拿出来做参数。 - 这里在增加用户时,往 request 里放一个 user 对象。
SuperEndPoint :
package com.cff.springbootwork.actuator.endpoint;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.endpoint.annotation.Endpoint;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.endpoint.annotation.ReadOperation;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.endpoint.annotation.Selector;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.endpoint.annotation.WriteOperation;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
@Endpoint(id = "super")
public class SuperEndPoint {
private Map<String, SuperUser> users = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@ReadOperation
public Set<String> users() {
return users.keySet();
}
@ReadOperation
public SuperUser usersIdentify(@Selector String arg0) {
return users.get(arg0);
}
@WriteOperation
public Set<String> set(String userName, String passwd) {
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes())
.getRequest();
if (request != null) {
SuperUser superUser = new SuperUser();
superUser.setUserName(userName);
superUser.setPasswd(passwd);
request.getSession().setAttribute("superUser", superUser);
users.put(superUser.getUserName(), superUser);
}
return users.keySet();
}
public static class SuperUser {
private String userName;
private String passwd;
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getPasswd() {
return passwd;
}
public void setPasswd(String passwd) {
this.passwd = passwd;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
还要将 Endpoint 注册为 bean
MvcEndPointConfig:
package com.cff.springbootwork.actuator;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.endpoint.condition.ConditionalOnEnabledEndpoint;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import com.cff.springbootwork.actuator.endpoint.SuperEndPoint;
@Configuration
@ServletComponentScan
public class MvcEndPointConfig {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnEnabledEndpoint
public SuperEndPoint superEndPoint() {
return new SuperEndPoint();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# 使用 Filter 对访问 actuator 做限制
上面已经说了,actuator 的接口要做保护,我这里就用 filter 对接口做最简单的保护。
- 对 / actuator/* 下所有路径做过滤, 并用 actuator.filter.switch 属性对 filter 做开关;
- 如果时 /actuator/super 路径的 post 操作,放行它,它将会往 request 中放一个对象;
- 其他 / actuator/* 下路径要判断 request 中有没有 user 对象,没有就返回错误提示。
ActuatorPermissionFilter :
package com.cff.springbootwork.actuator.filter;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.Filter;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.FilterConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebFilter;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
@WebFilter(urlPatterns = "/actuator/*", filterName = "actuatorPermissionFilter")
@Order(1) // 指定过滤器的执行顺序,值越大越靠后执行
public class ActuatorPermissionFilter implements Filter {
private String excludePath = "actuator/super";
@Value("${actuator.filter.switch}")
Boolean actuatorSwitch;
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) {
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) servletResponse;
if (actuatorSwitch && !(request.getRequestURI().endsWith(excludePath)
&& request.getMethod().equals(HttpMethod.POST.toString()))) {
Object user = request.getSession().getAttribute("superUser");
if (user == null) {
// 未登录,返回数据
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
response.setStatus(HttpStatus.OK.value());
response.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE);
mapper.writeValue(response.getWriter(), "您没有权限访问该接口,请使用自定义的登录接口设置superUser后使用!");
return;
}
}
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest, servletResponse);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
# Spring Boot Monitor 做监控页面
额外引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.pomit</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-monitor</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1</version>
</dependency>
2
3
4
5
Spring Boot Monitor (opens new window) 是一个对 Spring boot admin 监控工具做修改并适配单机的监控工具,完美继承了 Spring boot admin 的风格,直接使用 actuator 的指标进行显示。
Spring Boot Monitor (opens new window) 官网:https://www.pomit.cn/SpringBootMonitor (opens new window)
前面 maven 依赖中,已经说明依赖spring-boot-monitor,这时,无需其他配置.
访问http://127.0.0.1:8080/monitor, 自动跳转到 Spring Boot Monitor 的监控页面。
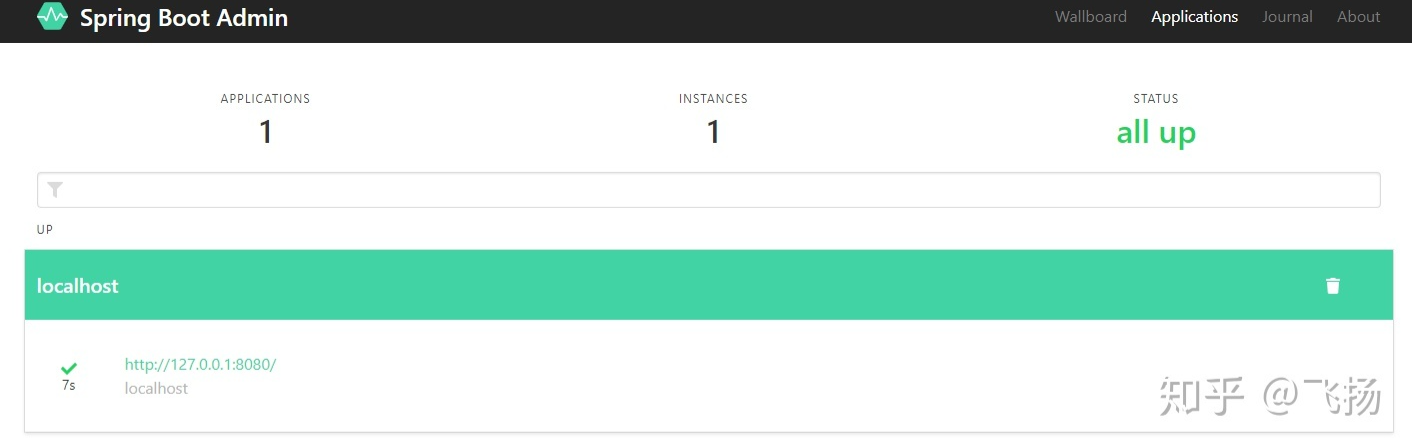
Spring Boot Monitor 的监控页面和 Spring boot admin 的一模一样,前端的功能也一模一样。
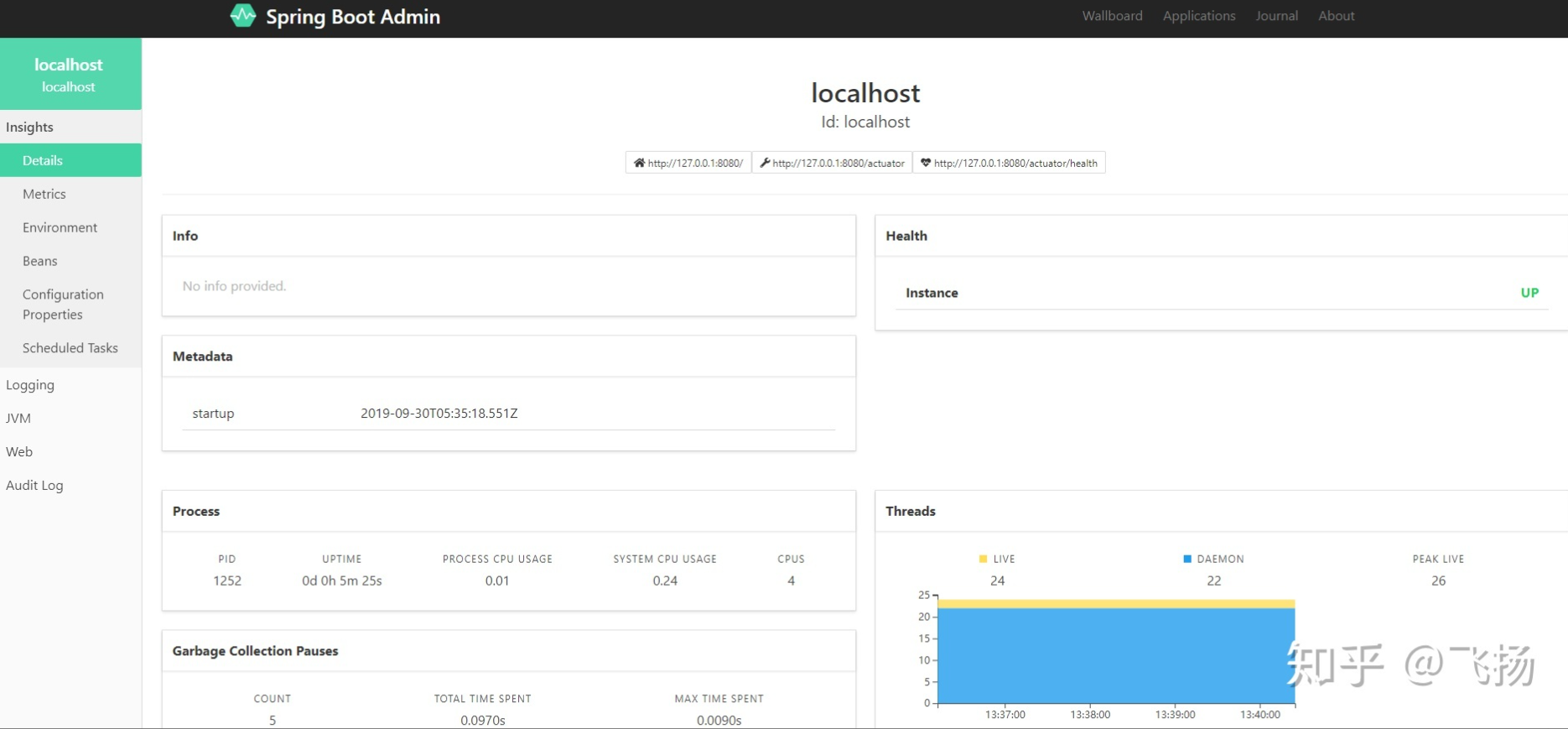
可以对 Spring boot 的各项指标一目了然,还可以进行简单的操作。
当然,如果 Spring boot actuator 的指标被限制了,它也拿不到相应的指标了,因为它是直接请求 actuator 接口的。
# 参考
- spring boot 2 使用 actuator 404 的问题 (opens new window)
使用 actuator 的指标进行显示。
Spring Boot Monitor (opens new window) 官网:https://www.pomit.cn/SpringBootMonitor (opens new window)
前面 maven 依赖中,已经说明依赖spring-boot-monitor,这时,无需其他配置.
访问http://127.0.0.1:8080/monitor, 自动跳转到 Spring Boot Monitor 的监控页面。
[外链图片转存中…(img-Naa3Zjvk-1642576052461)]
Spring Boot Monitor 的监控页面和 Spring boot admin 的一模一样,前端的功能也一模一样。
[外链图片转存中…(img-EaAoMOpX-1642576052462)]
可以对 Spring boot 的各项指标一目了然,还可以进行简单的操作。
当然,如果 Spring boot actuator 的指标被限制了,它也拿不到相应的指标了,因为它是直接请求 actuator 接口的。
# 参考
- 01
- idea 热部署插件 JRebel 安装及破解,不生效问题解决04-10
- 02
- spark中代码的执行位置(Driver or Executer)12-12
- 03
- 大数据技术之 SparkStreaming12-12
